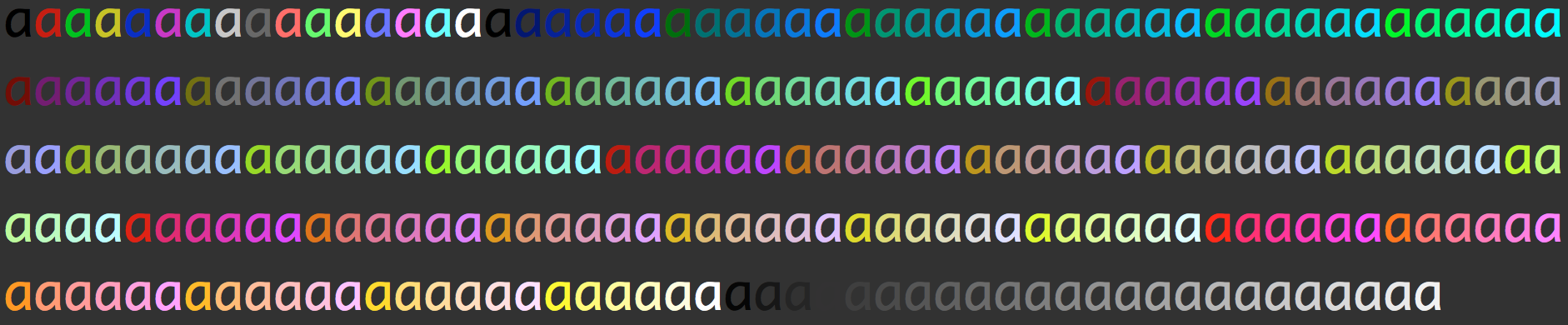Terminal string styling for Swift
Colors is a clean and focused solution for string styling in Swift. 
Usage
import Colors
print(Colors.blue("Blue string"))
print(Colors.Blue("Bright blue string"))
Addtionaly, you can compose modifiers:
print(Colors.blue(Colors.bgRed("Blue string with red background")))
Or define compositions for convenince:
infix operator >>> { associativity left }
func >>> <A, B, C>(f: B -> C, g: A -> B) -> A -> C {
return { x in f(g(x)) }
}
var error = Colors.bold >>> Colors.red >>> Colors.underline
print(error("There was an error"))
Installation
CocoaPods
Install cocoapods:
sudo gem install cocoapods
Then specify Colors in your Podfile:
pod 'Colors', '~> 0.1'
Finally run:
pod install
Styles
Bright/Normal Text Colors
Black/blackRed/redGreen/greenYellow/yellowBlue/blueMagenta/magentaCyan/cyanWhite/white
Bright/Normal Background Colors
BgBlack/bgBlackBgRed/bgRedBgGreen/bgGreenBgYellow/bgYellowBgBlue/bgBlueBgMagenta/bgMagentaBgCyan/bgCyanBgWhite/bgWhite
Text modifiers
blinkbolddimitalicunderlineinversehiddenstrikethrough
##API
Colors.<style>(text: String) -> String
Applies the specified <style> to the given text. For a list of styles check the styles section above.
Colors.underline("Underlined text")
Colors.colorText(text: String, color: Int) -> String
Requires 8-bit color support from the console.
Colors the letters of the given text with the specified color. color must be an integer from 0-255 representing an 8-bit color. For a list of 8-bit colors check here.
Generally useful if you want to color the text with very specific colors.
for i in 0...255 {
print(Colors.colorText("a", color: i), terminator: "")
}
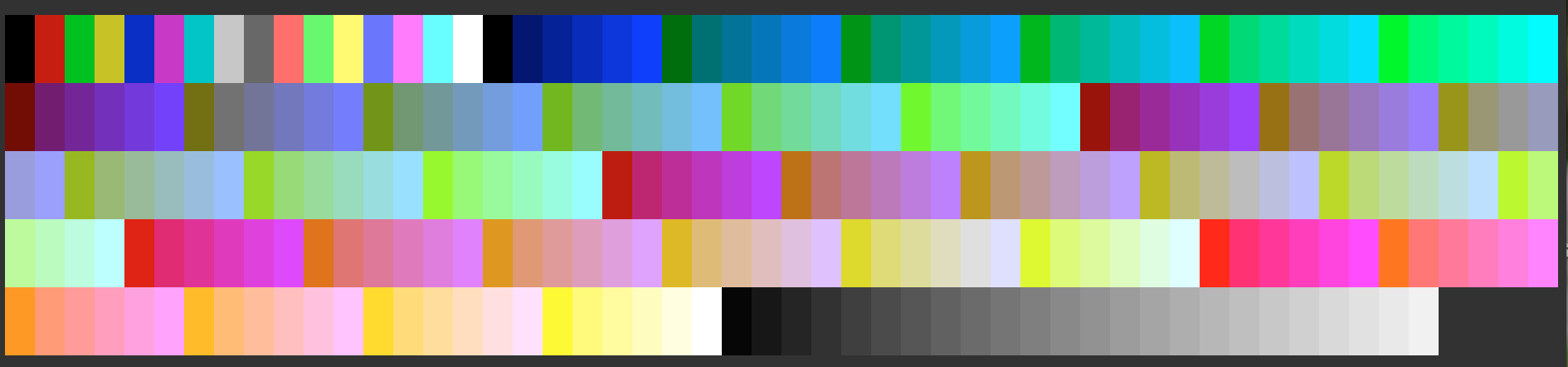
Colors.colorBg(text: String, color: Int) -> String
Requires 8-bit color support from the console.
Colors the background of the given text with the specified color. color must be an integer from 0-255 representing an 8-bit color. For a list of 8-bit colors check here.
Generally useful if you want to color the background with very specific colors.
for i in 0...255 {
print(Colors.colorBg(" ", color: i), terminator: "")
}
Colors.getTextColorer(color: Int) -> (String -> String)
Requires 8-bit color support from the console.
Returns a colorer function that will color the characters of the input string with the specified color.
Useful for defining your own style compositions with 8-bit colors.
infix operator >>> { associativity left }
func >>> <A, B, C>(f: B -> C, g: A -> B) -> A -> C {
return { x in f(g(x)) }
}
let warning = Colors.getTextColorer(23) >>> Colors.underline >>> Colors.BgRed
print(error("Some Warning"))
Colors.getBgColorer(color: Int) -> (String -> String)
Requires 8-bit color support from the console.
Returns a colorer function that will color the background of the input string with the specified color.
Useful for defining your own style compositions with 8-bit colors.
infix operator >>> { associativity left }
func >>> <A, B, C>(f: B -> C, g: A -> B) -> A -> C {
return { x in f(g(x)) }
}
let info = Colors.getBgColorer(23) >>> Colors.underline >>> Colors.Red
print(info("Some Warning"))
License
MIT © Paulo Tanaka